 Videos
Videos
Dawn Dufield, Ph.D. and Dominic Warrino, Ph.D. discuss their approach to ligand binding assays (LBAs) and hybrid mass spectrometry (Hybrid LC-MS/MS). What Makes a Good CRO for Bioanalysis? Are there any specific technologies that are more useful to have together? What is a Hybrid LC-MS/MS? Is Hybrid LC-MS/MS emerging…
 Scientific Posters
Scientific Posters
Please download this poster, “Monitoring immunogenicity of your candidate vaccine by ELISpot.” Vaccines_EIP2024_Poster_vfDownload…
 Scientific Posters
Scientific Posters
Please download this poster, “Performance of a method for quantifying progranulin as a target engagement biomarker for azp2006 in progressive supranuclear palsy.” PGRN_ADPD2024_PosterDownload…
 Scientific Posters
Scientific Posters
Please download this poster, “Flow Cytometric Analysis of Urine Cell 18-Color Immunophenotyping Panel.” 2024_WV_Carroll_SpectralUrineNMIBCDownload…
 Blogs
Blogs
Over the past decade, a continued discussion point has been the idea around analyzing samples on Ligand Binding Assay (LBA) platforms in singlet (one well) versus the standard duplicate analysis (Single sample added to two different wells). In the recent M10 Bioanalytical Method Validation Guideline issued for guidance in June…
 Blogs
Blogs
At KCAS Bio, we continuously seek ways to improve our processes with sound, logical, scientific, and business-related methods. One of these areas of evaluation has been sample preparation. We have improved various segments of bioanalysis (drying for unstable analytes, liquid handling, and plate-based assays for increased efficiency). We can also…
 April 16
- April 17
April 16
- April 17
Dive into the world of biotechnology at the German Biotechnology Days conference, where experts and innovators converge to explore cutting-edge research and technologies. This dynamic event features keynote speakers, workshops, and thematic sessions covering genomics, synthetic biology, regenerative medicine, and more. Attendees can network with industry leaders, discover investment opportunities,…
 Blogs
Blogs
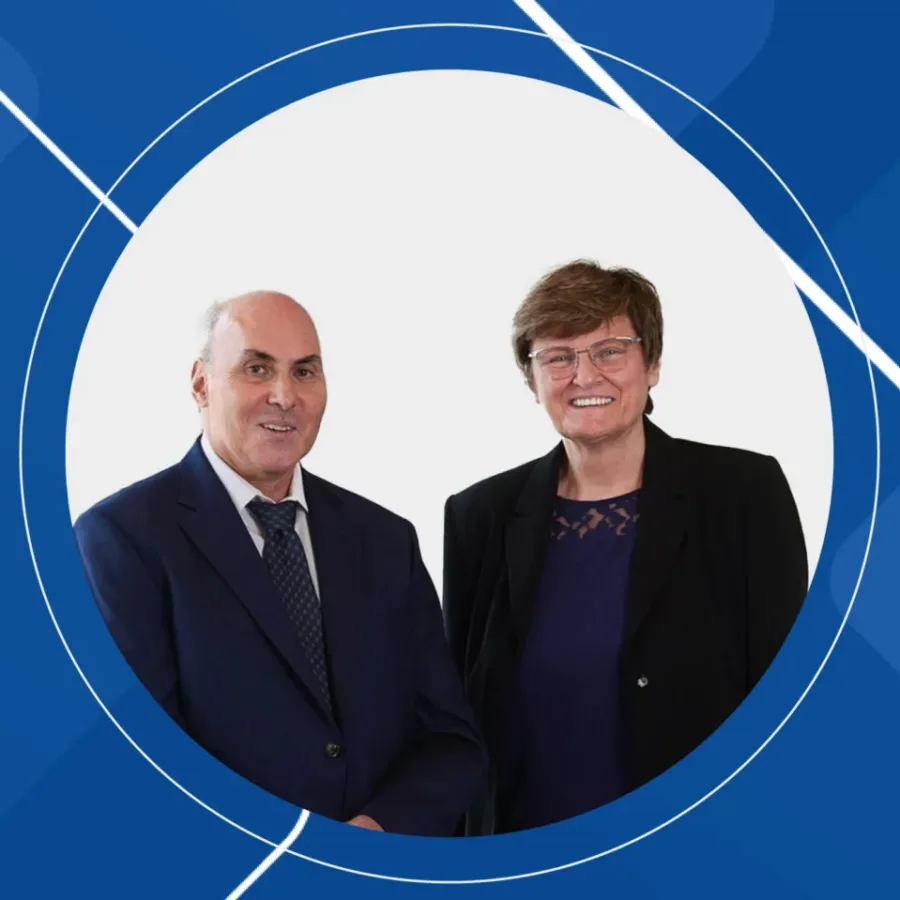
Pioneers of RNA Medicine: The Collaborative Journey of Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman The entire world benefited from their research in 2020. Despite facing skepticism, their collaborative efforts led to groundbreaking discoveries in RNA biology and immunology. They jointly received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2023.


